Consumer survey: The state of waiting in line (2024)
Frustration with waiting is rising, and patience is wearing thin. To help businesses adapt, Waitwhile surveyed 1,000 U.S. consumers to better understand how their expectations have evolved and identify the solutions they prefer to improve the waiting experience.

This post summarizes the findings from Waitwhile’s The State of Waiting in Line (2024), a study that examines how frequently consumers are waiting in line, how their expectations are evolving, and how businesses can adapt to improve the waiting experience. From rising frustration to growing demand for virtual queues and appointment scheduling, this year’s insights highlight the urgency for businesses to modernize their queue management strategies. To access the full report or download a copy, click here.
The universal pain point of waiting in line
Waiting in line remains a significant challenge for businesses as they contend with rising customer frustration and increasing competition for attention. Two years ago, Waitwhile launched The State of Waiting in Line, a first-of-its-kind study to explore how consumers perceive the persistent pain of physical queuing. The findings were stark: nearly 70% of consumers associated waiting in line with negative emotions like frustration, annoyance, and impatience. The scale of the issue became evident when we highlighted that Americans spend an estimated 37 billion hours each year waiting in lines - a phenomenon aptly described as a “timeless form of torture.”
Evolving customer expectations
Building on this foundation, our 2023 report shifted focus to uncover how consumer expectations were evolving and how businesses could address the dissatisfaction associated with traditional lines. The goal was to surface actionable solutions for improving the customer experience while keeping pace with shifting demands.
In The State of Waiting in Line 2024, we build upon the findings from the last two years to dive deeper into the evolving landscape of customer queuing, provide a fresh perspective on this enduring issue, and evaluate consumer expectations post-pandemic. As businesses navigate a rapidly changing consumer environment, the frustration of waiting in line persists as a major concern.
This report examines how consumers feel and act when they must wait in lines. Waiting in lines is a common experience - the survey found that 85% of consumers wait in line at least several times per month. For the third year in a row, retail is the industry where people wait in line the most. Customers spend more time in line at retail stores than at pharmacies, restaurants, banks, and doctors’ offices combined. The amount of time people wait in line at retail stores has increased by 61% since 2022 and 22% since 2023.
The rising costs of inefficient queues
As you’ll see in the following pages, waiting in line has a significant negative effect on how satisfied customers are and how well businesses perform. The research shows that consumers are becoming more frustrated with waiting, which leads to negative feelings, lower satisfaction, and even lost business. Nearly 40% of the people who avoid businesses because of lines will either go to a competitor or decide not to buy anything at all.
A roadmap for improving customer experiences
People are looking for ways to avoid traditional lines. Nearly 70% of consumers would prefer to schedule appointments instead of waiting in line, and 52% prefer virtual queues over physical lines. This year’s State of Waiting in Line discusses the benefits of virtual queue management systems and how they can make customers happier, more willing to wait, and even help businesses increase revenue.
The report also urges businesses to update how they manage lines. It provides strong evidence that using modern solutions like virtual queues and appointment scheduling can significantly improve customer experience, increase satisfaction, and lead to better business results.
Part 1: Waiting and impatience
Retail queues are 4X more common than in other industries
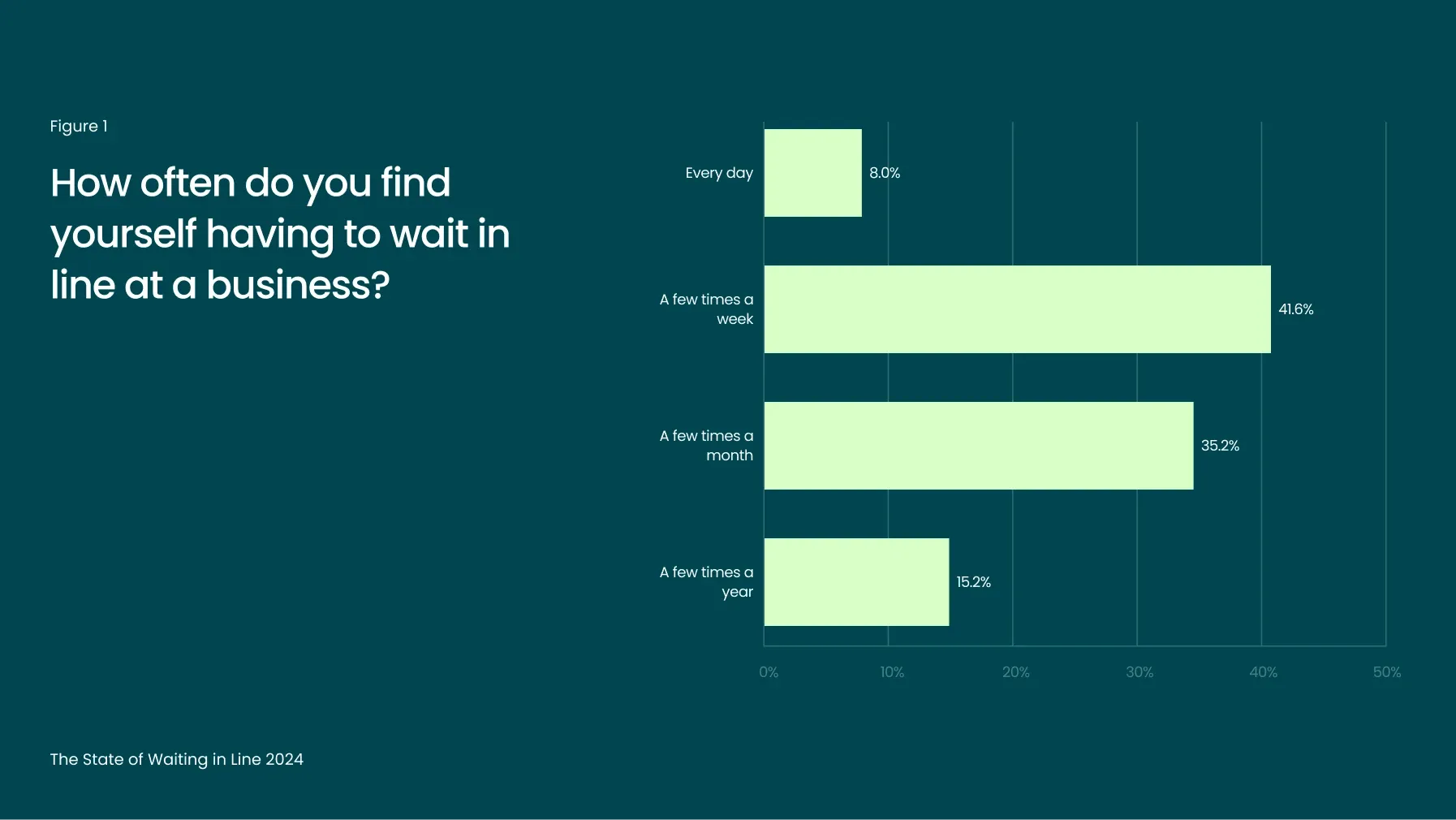
The 2024 findings highlight that waiting in line continues to be a common experience for the vast majority of consumers. 85% of respondents reported waiting in line at least a few times a month, with 50% facing this inconvenience weekly (Figure 1).
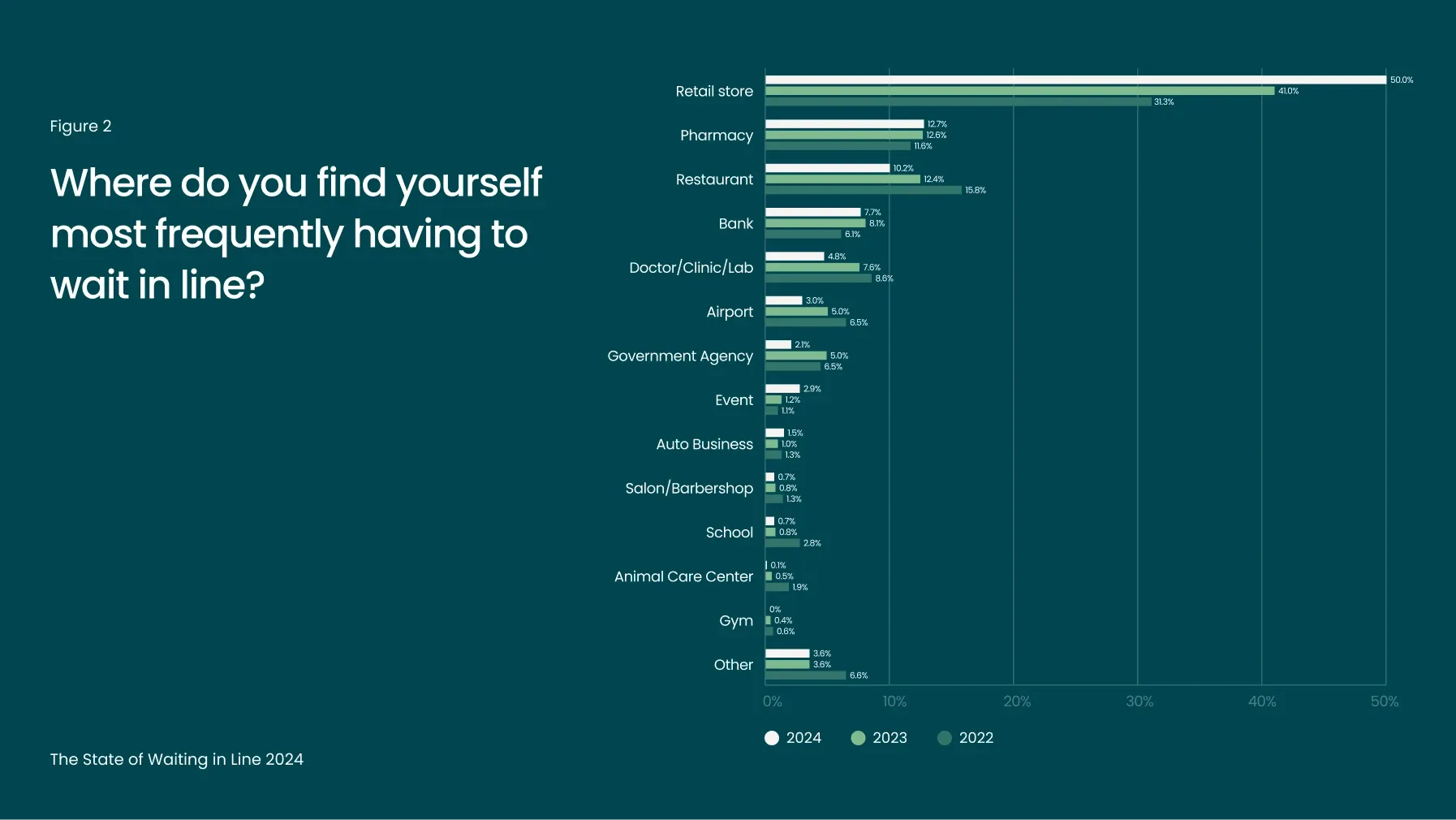
These statistics reveal a major disconnect between what consumers want and what businesses are delivering. For retail, the situation is even more pronounced: for the third year in a row, Waitwhile found that consumers face lines in retail more often than any other industry. Americans spend more time waiting in line at retail stores than at pharmacies, restaurants, banks, doctor’s offices and even airports combined (Figure 2). Time spent waiting in retail lines has surged by 61% since 2022 and 22% since 2023, underscoring retailers' struggles to adapt to the post-pandemic influx of in-store shoppers.
While demand for brick-and-mortar shopping has rebounded post-COVID, ongoing staff shortages have worsened wait times. A 2023 report by the National Retail Federation highlighted alarmingly high turnover rates in retail, making it difficult for stores to meet rising customer demand. With fewer staff to manage lines, adopting virtual queue management systems has become a critical strategy for minimizing wait times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Consumer frustration more than doubled since 2023
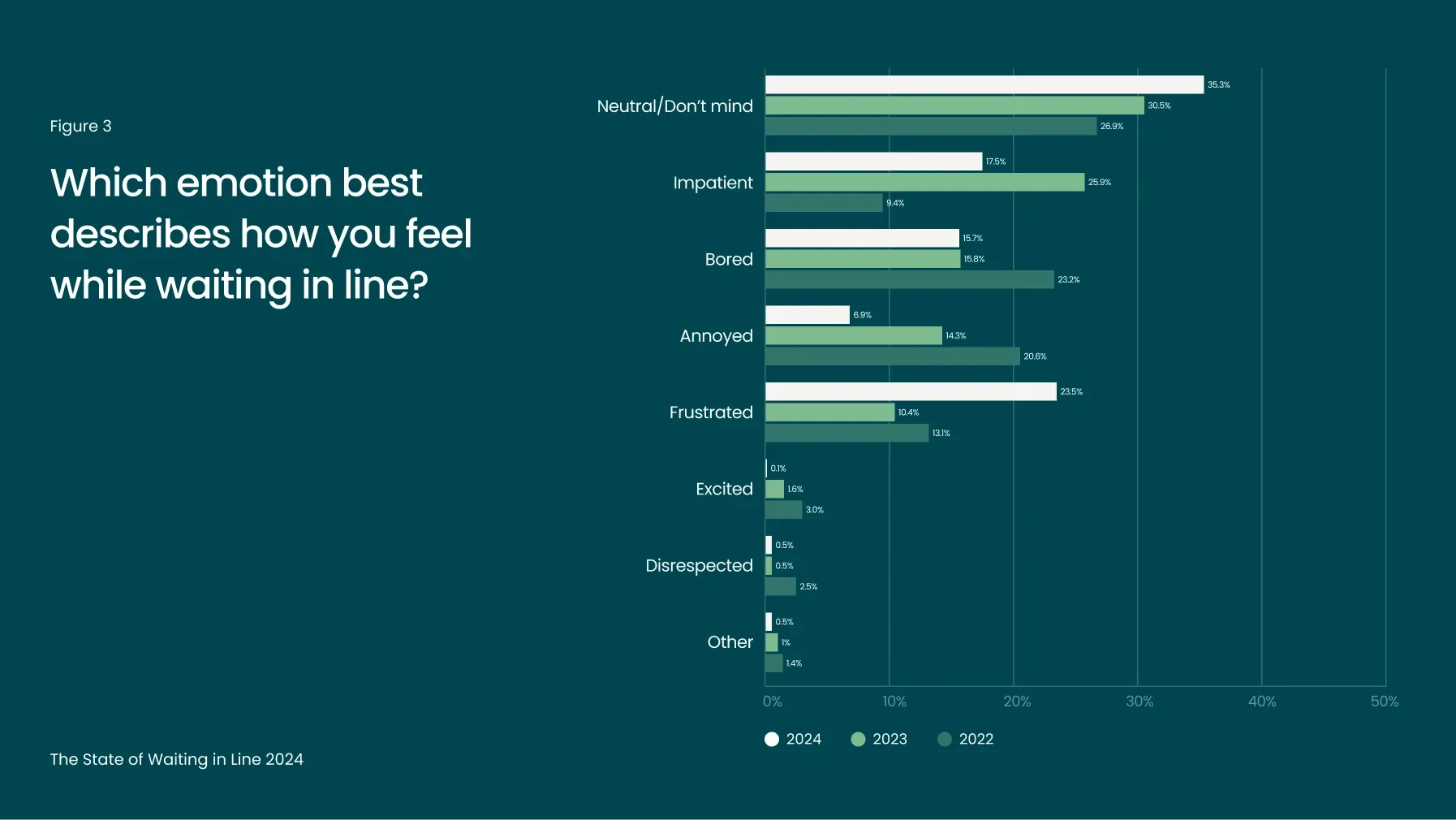
Humans aren’t naturally patient. Waiting has been called a “timeless form of torture” and the associated costs have been well-documented. The vast majority of consumers continue to associate waiting in line with negative emotions. Nearly 65% of respondents report feeling impatient, bored, annoyed, frustrated, or disrespected when they have to wait.
Last year, impatience skyrocketed by 176% year-over-year (YoY). This year’s findings suggest a shift from boredom and impatience toward frustration, which increased by 126% since 2023.
The psychological toll of waiting is well-recognized. Research from Frontiers in Psychology highlights that perceptions of time and emotional awareness are closely connected, with wasted time amplifying negative feelings like frustration and impatience. For businesses, these emotional responses often translate into lost revenue, as dissatisfied customers are more likely to abandon purchases or turn to competitors. While consumer impatience has eased slightly compared to last year, frustration with inefficient queuing remains a critical issue for businesses to address.
Higher frustration is contributing to greater consumer incivility. According to Waitwhile’s Employee Sentiment Report: Retail (2023), 68.5% of retail workers regularly deal with frustrated or angry customers, with long wait times cited as the top cause of customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, 73% of retail employees reported that long lines or extended waits are persistent challenges in their roles.Businesses are quickly running out of time to rethink their approach to customer queues. As both consumer impatience and employee dissatisfaction climb, the urgency to modernize queue management has never been greater. To meet rising expectations, businesses across industries must embrace innovative technologies that streamline queuing processes and deliver a smoother, more satisfying customer experience.
Nearly 70% of consumers prefer to schedule an appointment
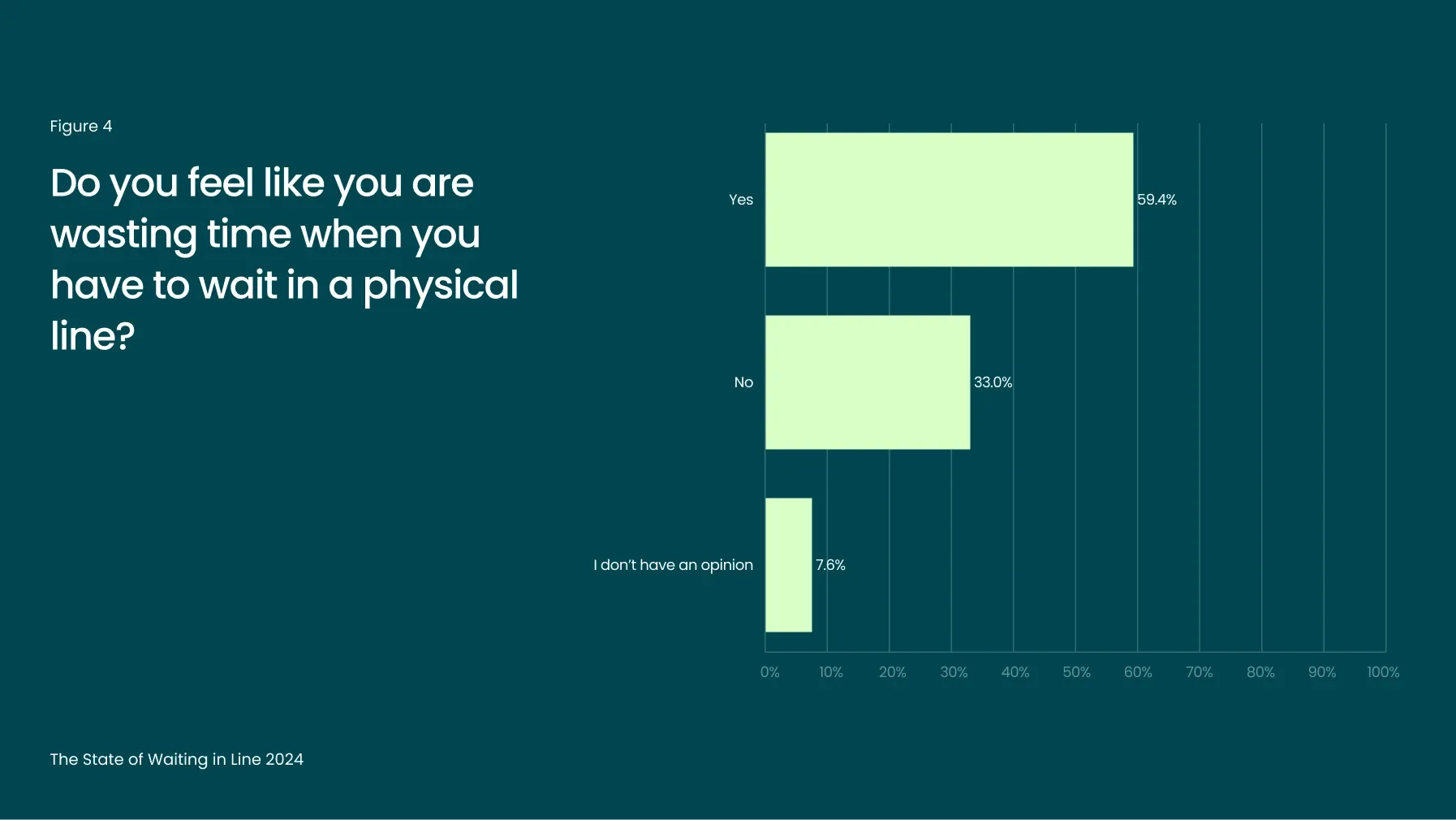
A significant 59% of consumers feel that waiting in line is a waste of their time (Figure 4). This perception is closely tied to the negative emotions associated with queuing, such as frustration, boredom, and impatience (Figure 3). These emotions not only contribute to a poor customer experience but also diminish the perceived value of the service or product being offered.
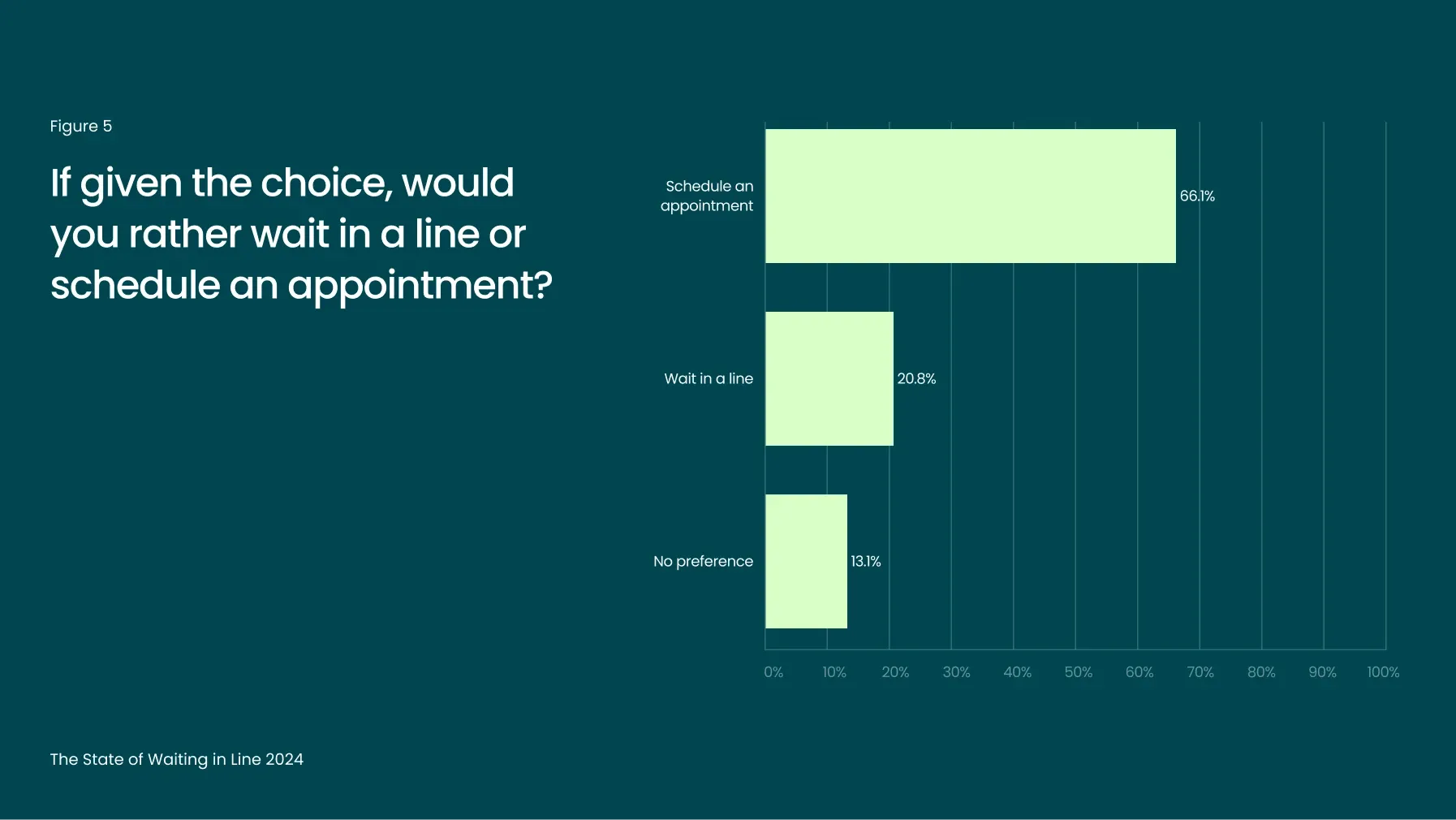
The data reveals a clear demand for more efficient alternatives. Nearly 70% of respondents prefer scheduling an appointment to waiting in line (Figure 5), signaling a shift toward structured and predictable service interactions. Businesses that implement appointment-based systems can increase customer satisfaction while improving operational efficiency. By minimizing the need for physical queues, companies can deliver a better overall experience and reduce stress on frontline staff, helping to prevent negative customer interactions.
These findings echo broader research on consumer impatience, highlighting the critical need for convenient alternatives to traditional queuing methods.
Part 2: The impacts on business
3 out of 5 customers leave lines before their turn
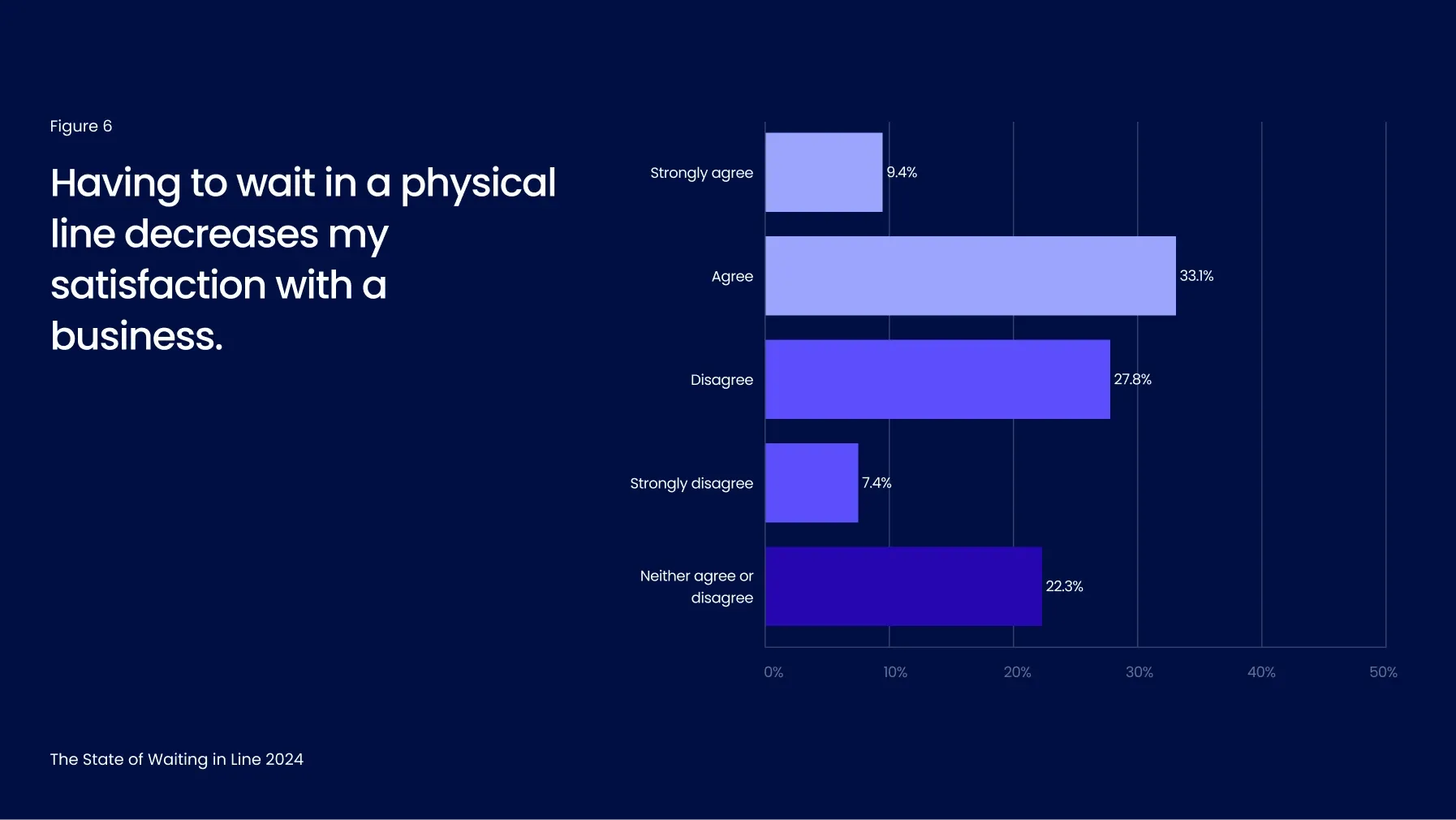
Customer satisfaction is heavily impacted by the presence of physical lines. According to this year’s findings, more than 43% of consumers report feeling less satisfied with businesses that require them to wait in a queue (Figure 6).
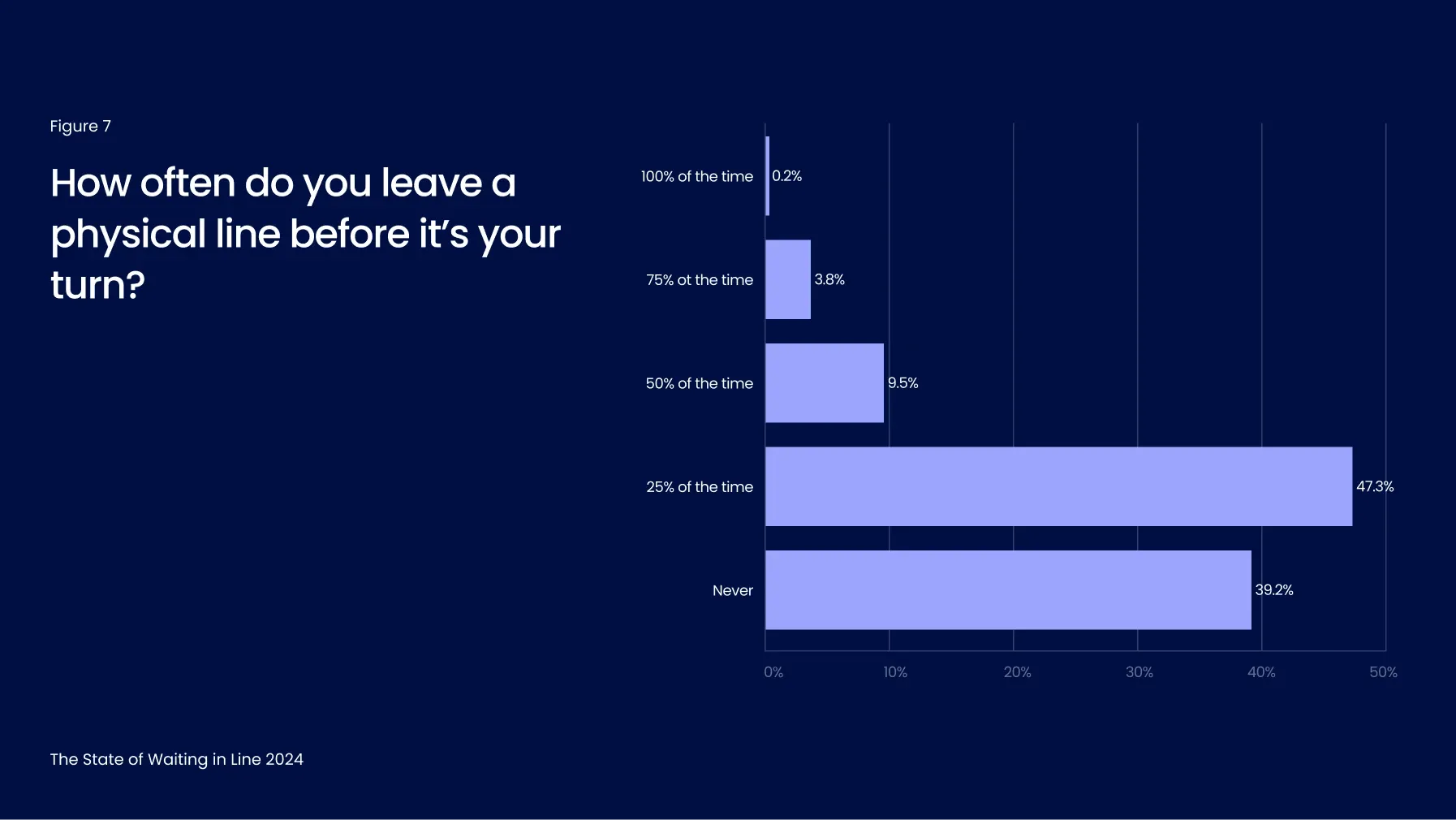
This dissatisfaction has tangible consequences, with physical lines often leading to reduced customer throughput. 61% of respondents admitted to leaving a line before reaching their turn, while approximately 1 in 7 doing so regularly, walking away over half the time (Figure 7).
Long lines are more than just an inconvenience - they result in lost business. When customers abandon a queue, it’s not only a single missed transaction but also an erosion of trust and loyalty. Consumers are less likely to return to businesses where they’ve had a frustrating experience. Research conducted by Ryan Buell, a Harvard Business School professor, emphasizes how such behavior not only affects the customer but also severely impacts the service provider’s bottom line.
The link between physical queues and negative business outcomes underscores the urgent need for businesses to modernize customer management systems. Implementing virtual queues and appointment scheduling solutions can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, reduce abandonment rates, and protect long-term revenue.
80% of consumers avoid going to a business because of lines
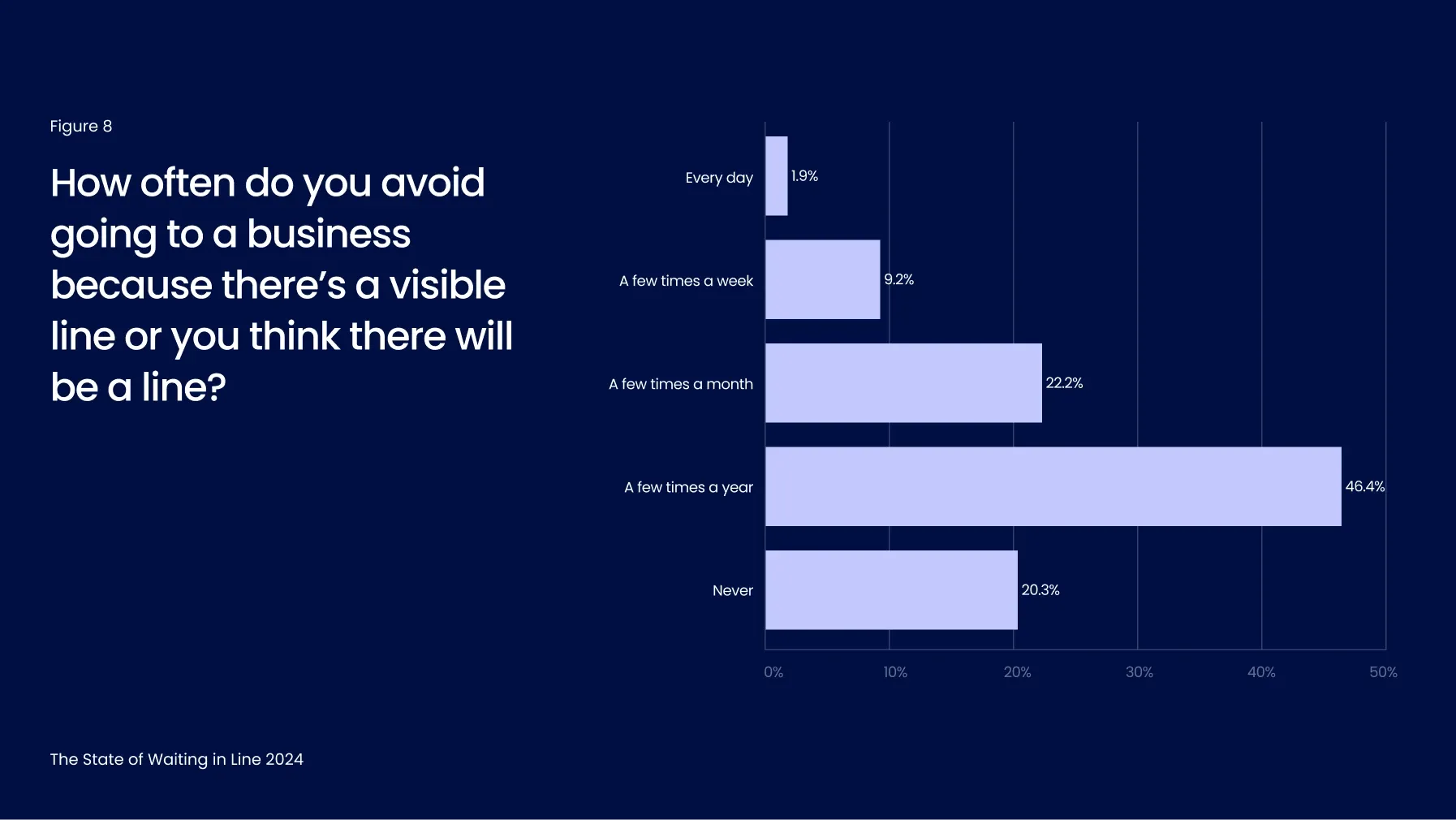
Even the mere expectation of having to wait has a powerful effect on consumers. Waitwhile’s survey this year found that 80% of consumers avoid going to businesses because they see a line or anticipate one (Figure 8).
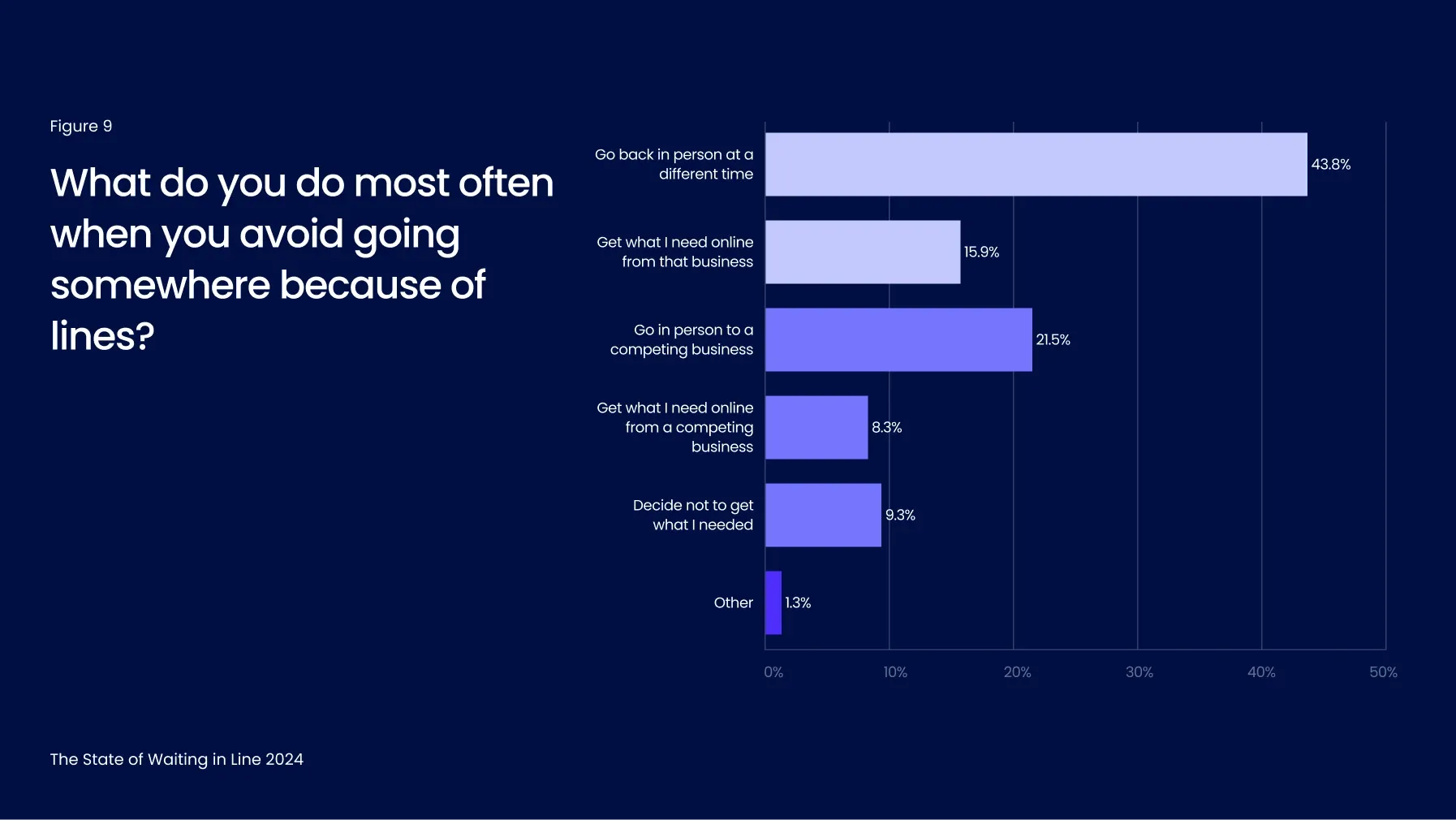
Among those who change their plans due to queues, more than 60% will eventually return to the business, either in person or online, to complete their purchase or service. Alarmingly, nearly 40% will go to a competitor or abandon their purchase altogether to avoid the inconvenience of waiting (Figure 9). To bypass lines, consumers are increasingly turning to online shopping. While some use the business’s own online platform, a growing number opt for online competitors offering more seamless experiences.
This data offers clear evidence that queues negatively affect businesses' bottom lines. The majority of consumers dislike waiting so much that they actively alter their plans to avoid it. Businesses with persistent physical queues but no alternative solutions - such as virtual queues or appointment scheduling - are out-of-step with consumer expectations and risk damaging their reputations and losing revenue.
Part 3: Virtual queues
52% of consumers prefer virtual queues
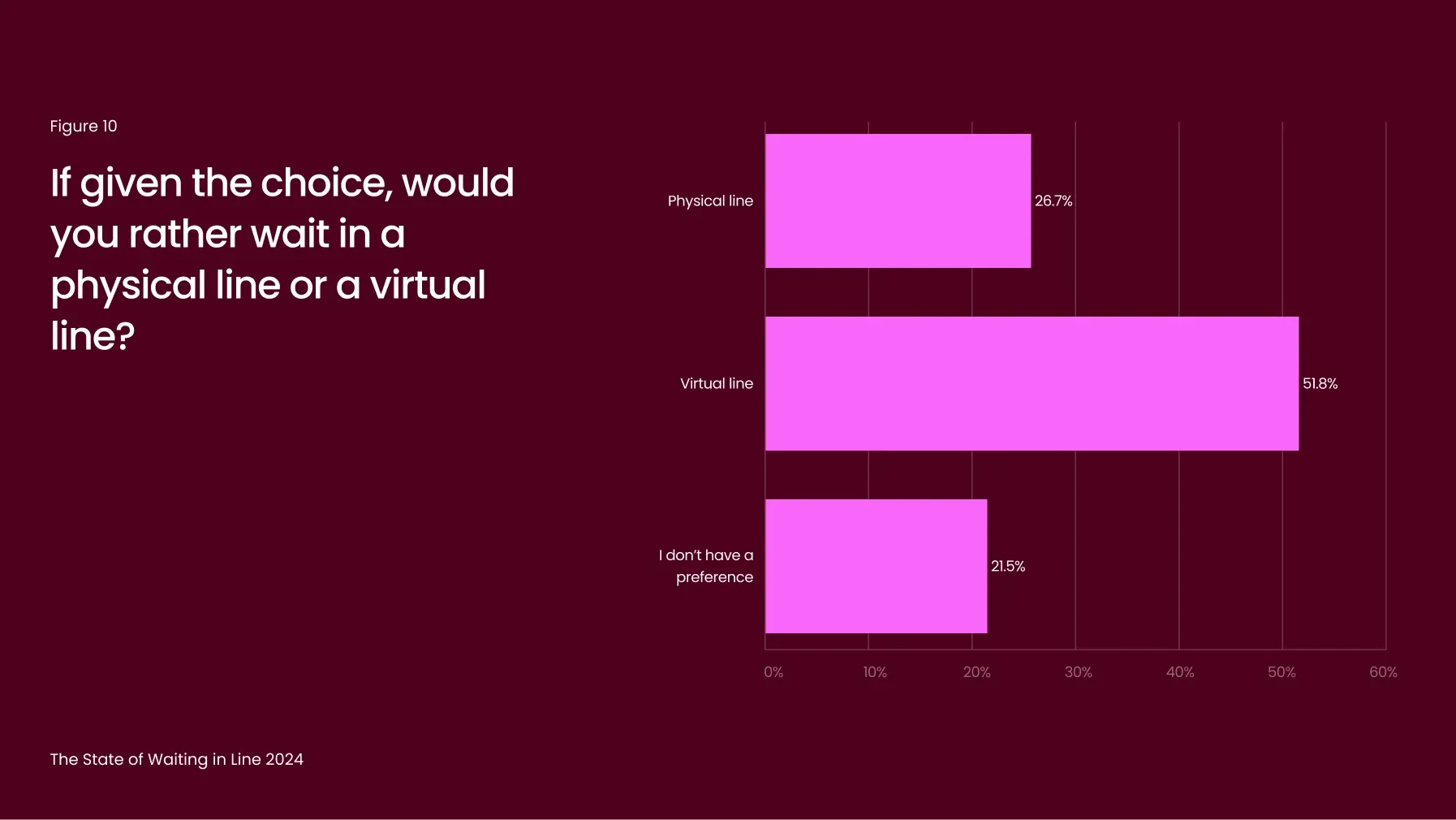
Physical lines continue to harm business outcomes, making it essential for companies to adopt alternatives like virtual queues. These systems let customers track their wait times, join queues from their devices, and wait remotely - whether at home, in their car, or while browsing elsewhere. By giving customers control and allowing them to use their time productively, virtual queues transform the waiting experience, often making it feel shorter or eliminating the perception of waiting altogether.
This year, 52% of consumers expressed a preference for virtual queues over traditional ones (Figure 10), highlighting strong demand for these solutions. Yet, many businesses still rely on outdated queuing methods: more than 75% of respondents reported waiting in a physical line during their most recent experience (Figure 11), illustrating a missed opportunity for modernization.
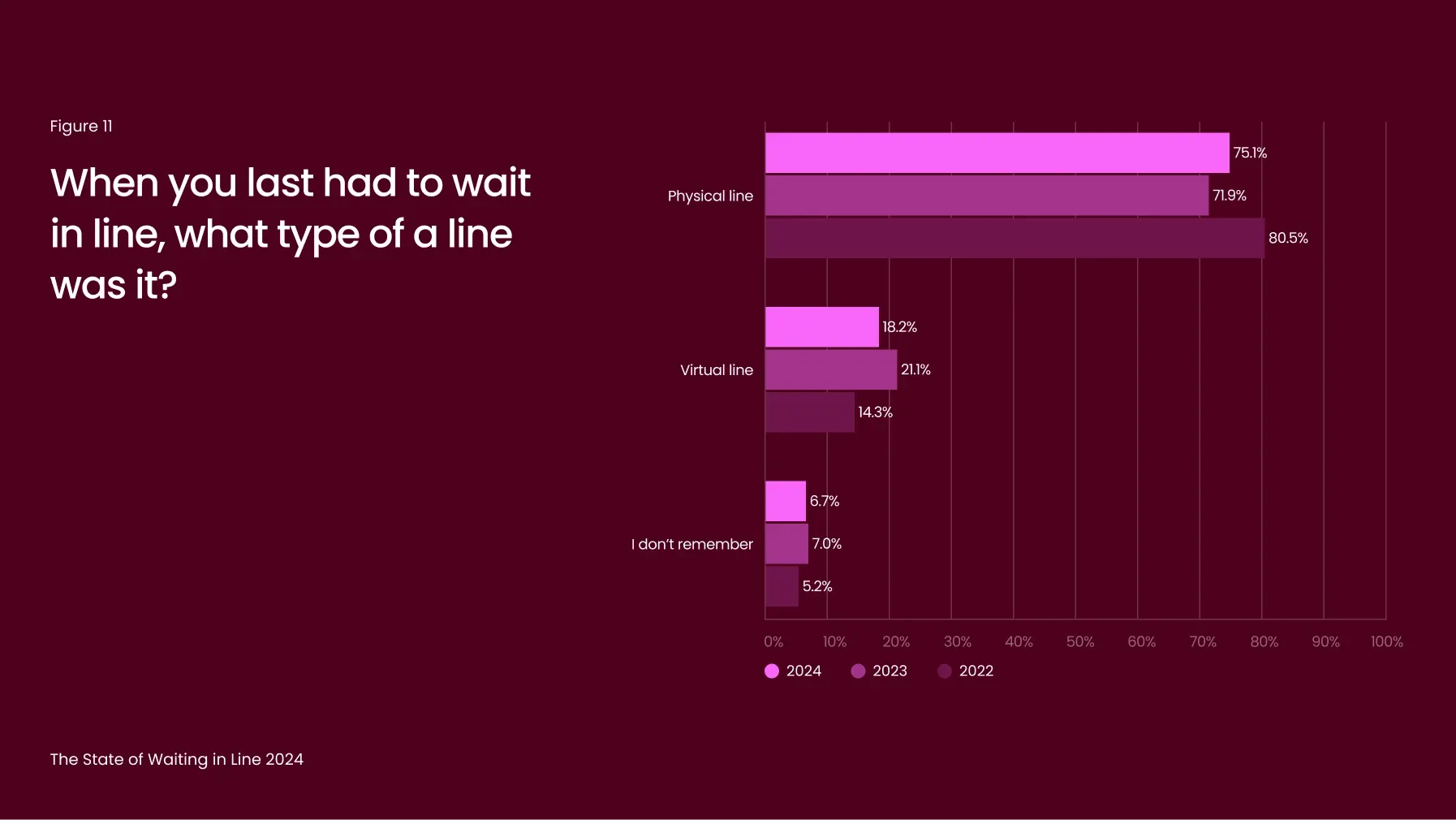
While 2023 saw incremental progress in adopting digital queuing solutions, the momentum appears to be slowing. Virtual queue adoption declined from 21% to 18% compared to last year (Figure 11). This drop underscores the need for businesses to prioritize innovation and close the gap between consumer expectations and reality. With a clear link between physical queues and poor customer satisfaction, accelerating the adoption of virtual queuing solutions is vital for improving customer experiences and maintaining competitiveness.
54% of consumers are willing to wait longer in a virtual queue
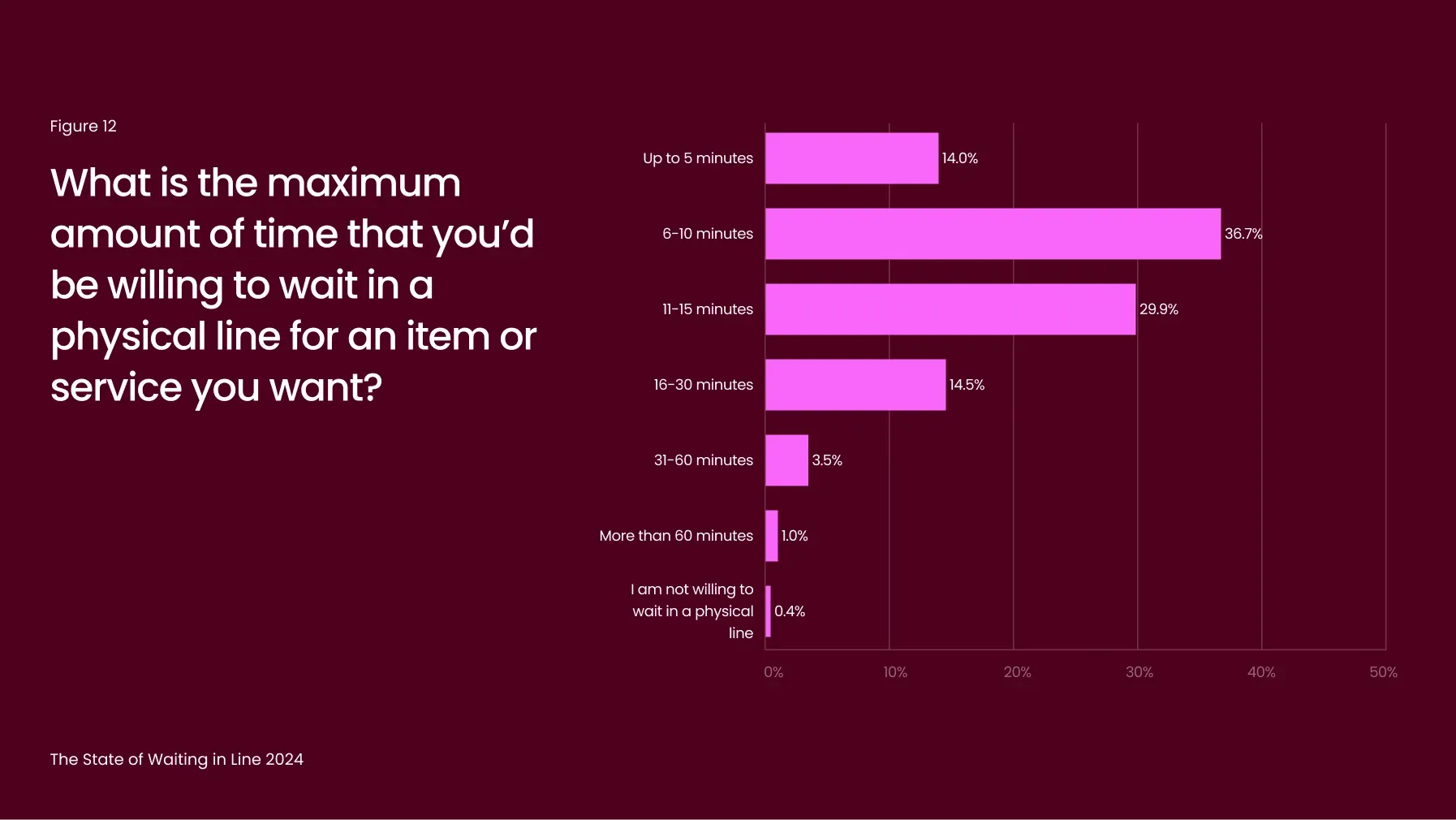
Consumers’ willingness to wait longer in virtual queues highlights a key advantage of these systems. While 80% of consumers are only willing to wait up to 15 minutes in a physical line for a product or service (Figure 12), patience increases significantly with virtual queues. Only 5% of consumers are willing to wait more than 30 minutes in a physical line, but 24% are willing to wait an extra 30 minutes or more in a virtual queue.
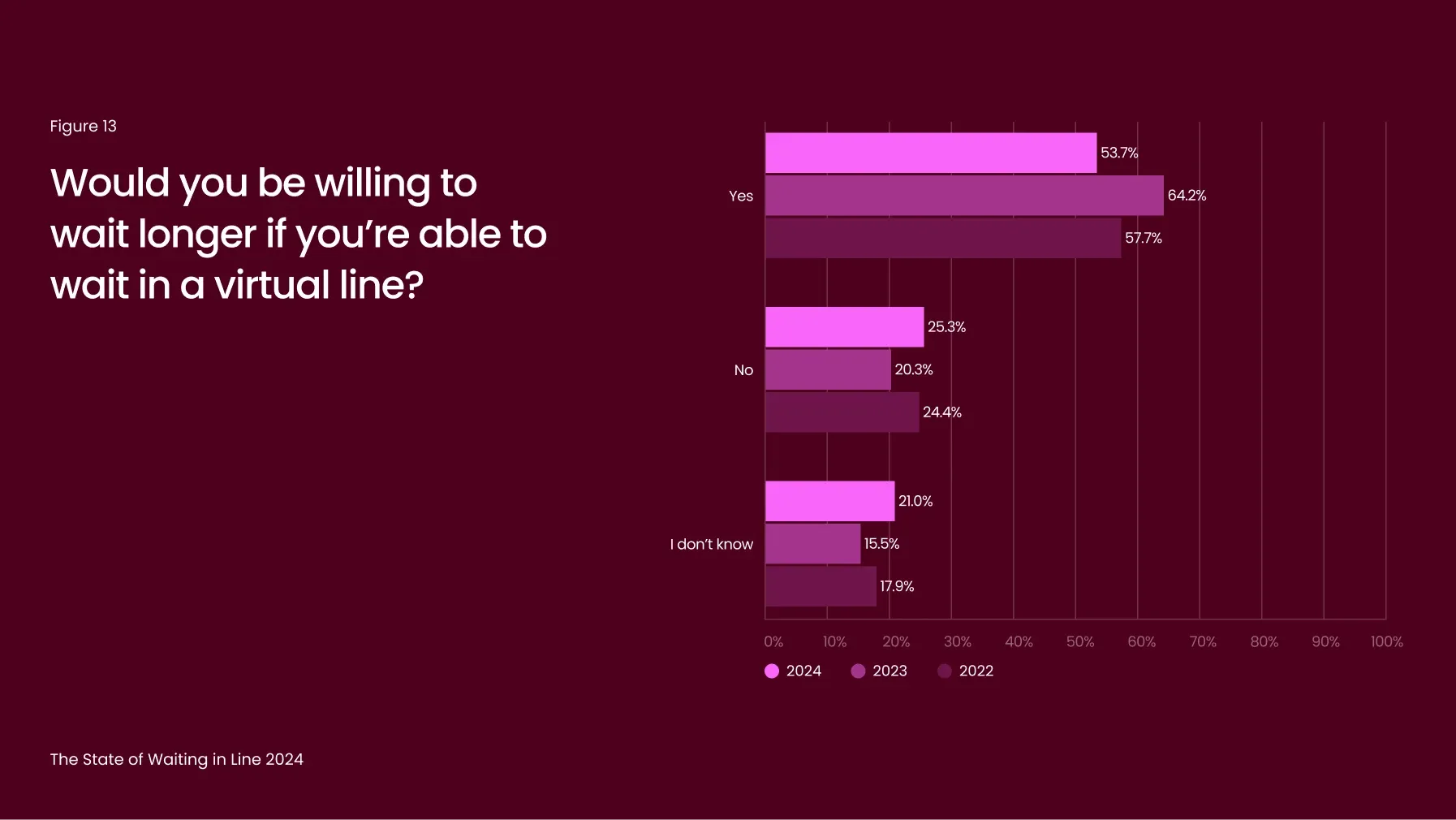
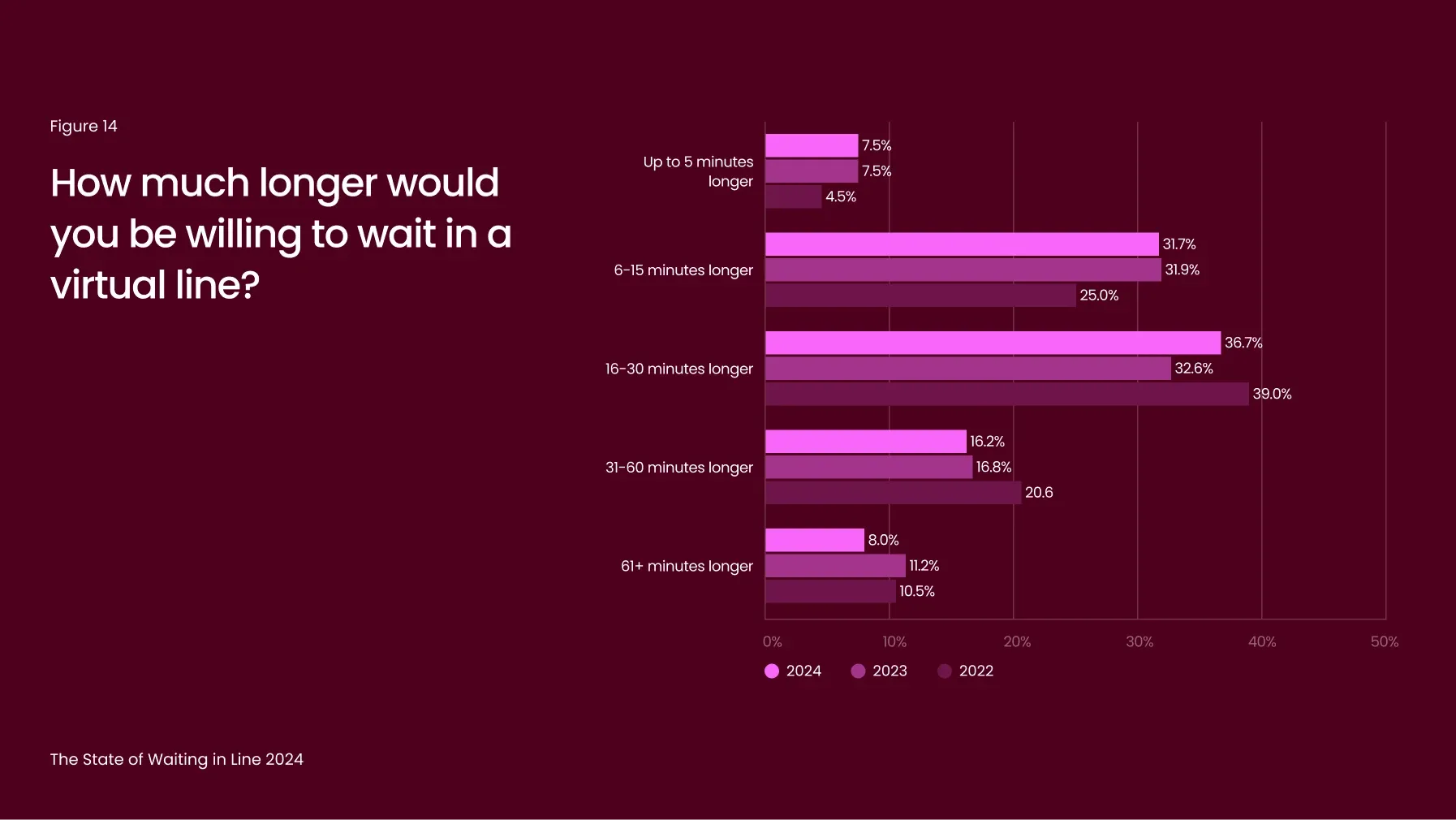
Overall, 54% of respondents said they’d extend their wait in a virtual queue (Figure 13), with 61% willing to wait at least 15 minutes longer than they would in person and nearly 25% willing to wait 30 minutes or more (Figure 14).
This flexibility makes virtual queues a powerful tool for businesses to alleviate customer frustration. Even as overall consumer frustration with waiting doubled year-over-year (Figure 3), virtual queues help reduce the discomfort associated with physical lines. However, managing virtual experiences effectively is essential, as consumers report feeling slightly more impatient with virtual wait times this year compared to last.
Although patience for virtual queues has dropped slightly by 10 percentage points (Figure 13), they remain the preferred alternative. Virtual queues allow customers to use their waiting time productively, transforming idle time into useful time and minimizing the perception of inconvenience.
For businesses, adopting virtual queue management solutions is a critical step to improving customer satisfaction and retention. Virtual systems give customers flexibility, reducing the need for costly operational changes, such as hiring additional staff or expanding service capacity. They represent a high-impact, low-effort solution to meet modern expectations and deliver better service experiences.
More than 40% of consumers will continue shopping while waiting in a virtual queue
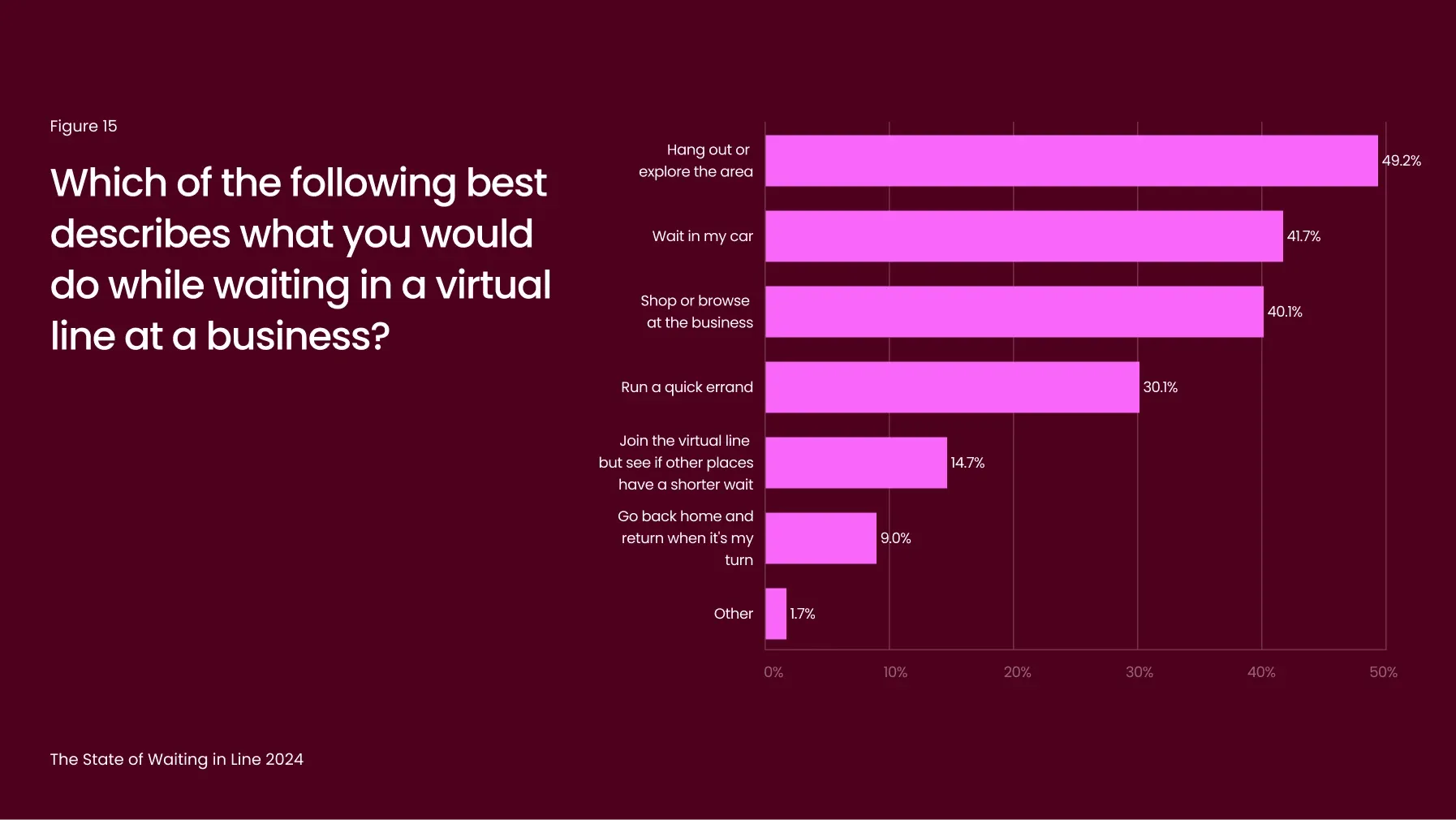
Virtual queues don’t just address long wait times - they also provide businesses with opportunities to increase revenue. This year, 41% of consumers reported that they continue shopping or browsing while waiting in a virtual queue, up from 38% in 2023 (Figure 15). This behavior allows businesses to engage customers during their wait time, turning what would otherwise be idle time into an opportunity for additional sales.
In sectors like retail and hospitality, where foot traffic directly drives revenue, virtual queues enable a more seamless and enjoyable customer experience. Studies show that businesses adopting virtual queuing systems benefit from increased sales, customers were more likely to make additional purchases while waiting. By capitalizing on this waiting period, businesses can enhance customer engagement and boost revenue.
Conclusion
The 2024 State of Waiting in Line findings underscore the critical need for modern queue management in today’s business landscape. While the COVID-19 pandemic temporarily shifted consumer behavior, people are returning to brick-and-mortar businesses with clear goals in mind. They are willing to wait for what they want but increasingly expect businesses to respect their time.
The data highlight the importance of prioritizing modern queue management solutions to stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations. Embracing new technology can transform waiting from a source of frustration into an opportunity for greater customer engagement, higher satisfaction, and ultimately, business growth.
While the adoption of virtual queues has slowed down slightly since 2023, these systems still offer businesses a way to reduce frustration and cater to customer needs. To adapt to these shifting consumer demands, businesses must implement solutions that minimize the negative impacts of waiting:
- Virtual queues extend customer patience by giving them the freedom to use their waiting time productively, such as continuing to shop or browse. This flexibility turns wasted time into productive time, making virtual queues a powerful tool for reducing frustration.
- Appointment scheduling systems offer predictability and control, a feature preferred by nearly 70% of consumers. These systems help businesses manage customer flow more efficiently, reducing wait times for everyone.
By adopting innovative queue management solutions, businesses can reduce customer dissatisfaction, prevent lost revenue from abandoned purchases, and create a seamless, enjoyable customer experience. These systems not only cater to the modern consumer’s need for intentionality but also strengthen brand loyalty and operational efficiency.
The data make it clear - modernizing queue management is essential for long-term business success. Solutions like virtual queues and appointment scheduling represent a win-win: happier customers and a healthier bottom line.
